Modern technology has revolutionized how we charge our devices, making wireless charging an essential part of our lives. Gone are the days of tangled cords and frantic searches for charging stations. This technology, based on electromagnetic induction, allows for seamless power transfer between a device and a charging pad, simplifying daily tasks. In this article, we explore the fascinating world of wireless charging, including its mechanisms, underlying technology, and practical applications. How does wireless charging work? It operates on electromagnetic induction, enabling energy transfer without physical connectors.
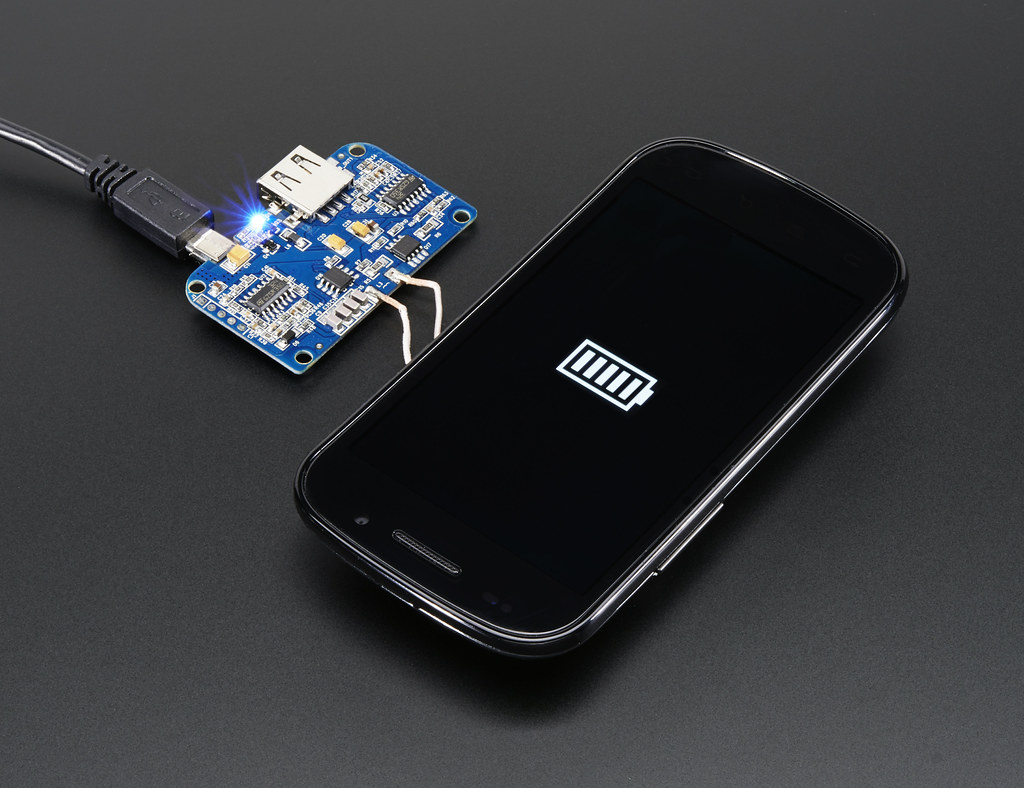

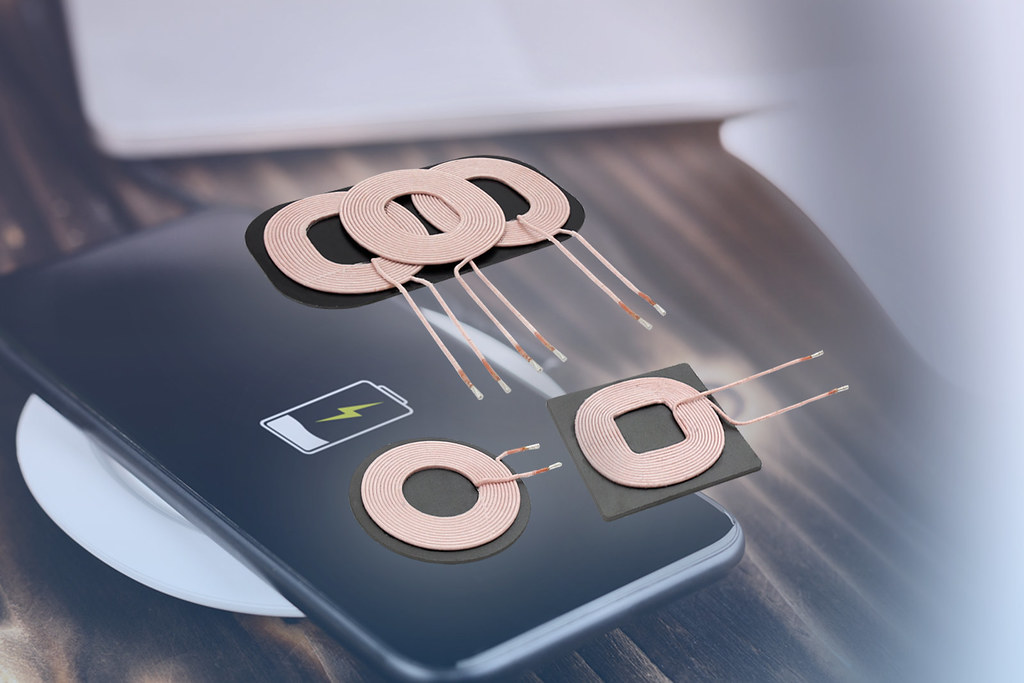
At the heart of this system are two coils: a transmitter coil in the charging pad and a receiver coil within the device. When a device is placed on the pad, the transmitter coil generates an alternating current, creating a changing magnetic field. This field induces an alternating current in the receiver coil, allowing the device to charge. The receiver coil then converts this induced current into direct current, powering the device’s battery. The interaction between these components is intricate and fascinating.
The quality and efficiency of the transmitter coil are crucial for minimizing energy loss during transfer. Similarly, the receiver coil’s ability to convert the magnetic field into usable energy significantly impacts charging speed and effectiveness. Continuous advancements in both transmitter and receiver technology promise improvements in efficiency and charging capabilities. For example, the UTS-1 Invisible Wireless Charger by Kew Labs offers innovative integration into furniture, providing a neat appearance without sacrificing functionality. To further demystify wireless charging, it’s essential to understand the science behind these mechanisms.
The process hinges on a principle known as Faraday’s Law of Induction, which illustrates how a changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a conductor. In practical terms, when the charger is activated, the transmitter coil generates a magnetic field that excites electrons in the receiver coil. This interaction is what makes charging possible without the need for direct electrical contact. Notably, industries beyond personal electronics are beginning to explore wireless charging technologies. Applications in automotive and healthcare, among others, are becoming increasingly common.
For example, the automotive industry is exploring the integration of wireless chargers into car designs, allowing passengers to power their devices without dealing with cords. Similarly, healthcare facilities are adopting wireless charging to streamline operations and enhance user experience. Exploring different types of wireless charging technologies reveals that it is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it includes various technologies catering to different needs and applications. Among the most common are tightly-coupled inductive charging, loosely-coupled resonant charging, and uncoupled radio frequency (RF) charging.
1.Tightly-Coupled Inductive Charging (Qi Standard). This is perhaps the most recognized form of wireless charging, popularized by the Qi standard widely adopted in smartphones and other portable devices. Tightly-coupled inductive charging requires close physical alignment between the charging pad and the device for efficient energy transfer. The charging pad contains a transmitter coil that generates an electromagnetic field when powered. When a compatible device is placed on top, the receiver coil captures this field, inducing an electric current that charges the device’s battery.
The Qi standard’s popularity can be attributed to its reliable performance and ease of use, with many leading smartphone manufacturers incorporating this technology into their devices. The convenience of simply placing a device on a pad has made it a go-to solution for users seeking a straightforward charging experience.
2.Loosely-Coupled Resonant Charging.This innovative technology pushes the boundaries of wireless charging by allowing energy transfer over greater distances and with more forgiveness regarding alignment. Loosely-coupled resonant charging utilizes resonant coils tuned to specific frequencies, enabling effective energy transfer even if devices are not perfectly aligned. This flexibility opens up exciting possibilities, particularly in environments where multiple devices need to be charged simultaneously.Automotive manufacturers, for instance, can use this technology to allow vehicles to charge while parked over a larger pad, eliminating the need for precise placement of devices.
3. Uncoupled Radio Frequency (RF) Charging. At the forefront of wireless charging innovation, uncoupled RF charging represents a significant leap forward. Unlike traditional methods that require physical connection, RF charging enables power transfer over considerable distances using radio waves. This technology is particularly appealing for its true wireless freedom—devices can charge without being tethered to a specific spot.The Cota Power Transmitter, for example, exemplifies this technology by using phased array antennas to direct RF waves toward compatible devices, allowing for continuous charging as long as the device is within range. Real-world applications of RF charging could transform smart homes and public spaces, providing seamless power access without the clutter of cables.
Understanding the Role of Magnetic Fields
The generation of magnetic fields is essential in wireless charging technologies. The magnetic field produced by the transmitter coil excites electrons in the receiver coil, enabling the conversion of magnetic energy into electrical energy. This process, governed by Faraday’s Law, facilitates the convenient charging of devices without direct electrical contact. As wireless charging technology evolves, the capabilities of both transmitter and receiver coils are being enhanced to increase efficiency and broaden applications, paving the way for a future where charging becomes even more integrated into our environments.

The potential for innovation in wireless charging technology is vast, with emerging solutions like integrated wireless charging surfaces for kitchens and workspaces. Homeowners are increasingly adopting these designs to create a seamless and functional living area, exemplifying how technology can enhance everyday life. In conclusion, wireless charging is not just a convenient feature; it represents a significant advancement in how we interact with technology. Understanding the mechanics behind wireless charging unveils a world of possibilities that extend beyond mere convenience. As we explore various technologies and their applications, we come to appreciate how they will shape our future interactions with devices.Embracing this technology could lead to a cleaner, more efficient, and increasingly connected world, where the need for cables becomes a thing of the past.
As we delve deeper into the world of wireless charging, it is crucial to evaluate both its benefits and challenges and how these factors affect its integration into our daily lives. Wireless charging represents more than just a modern convenience; it signifies a significant shift in how we power our devices, accompanied by complexities that must be understood.
Evaluating the Benefits of Wireless Charging
One of the most compelling advantages of wireless charging is the elimination of clutter. Gone are the days of tangled cables and searching for the right charger. For users with multiple devices, the convenience of simply placing their gadgets on a charging pad is a game changer. Not only does this simplify the charging process, but it also creates a cleaner aesthetic in homes and offices.
Moreover, many modern wireless chargers are designed to integrate seamlessly into furniture and everyday environments. Imagine a kitchen countertop that can wirelessly charge your smartphone while you prepare meals. This integration enhances both functionality and aesthetics, making technology an unobtrusive part of our lives. Wireless charging stations are now common in popular locations like cafes, airports, and public transport systems, allowing users to power their devices without the hassle of cords.
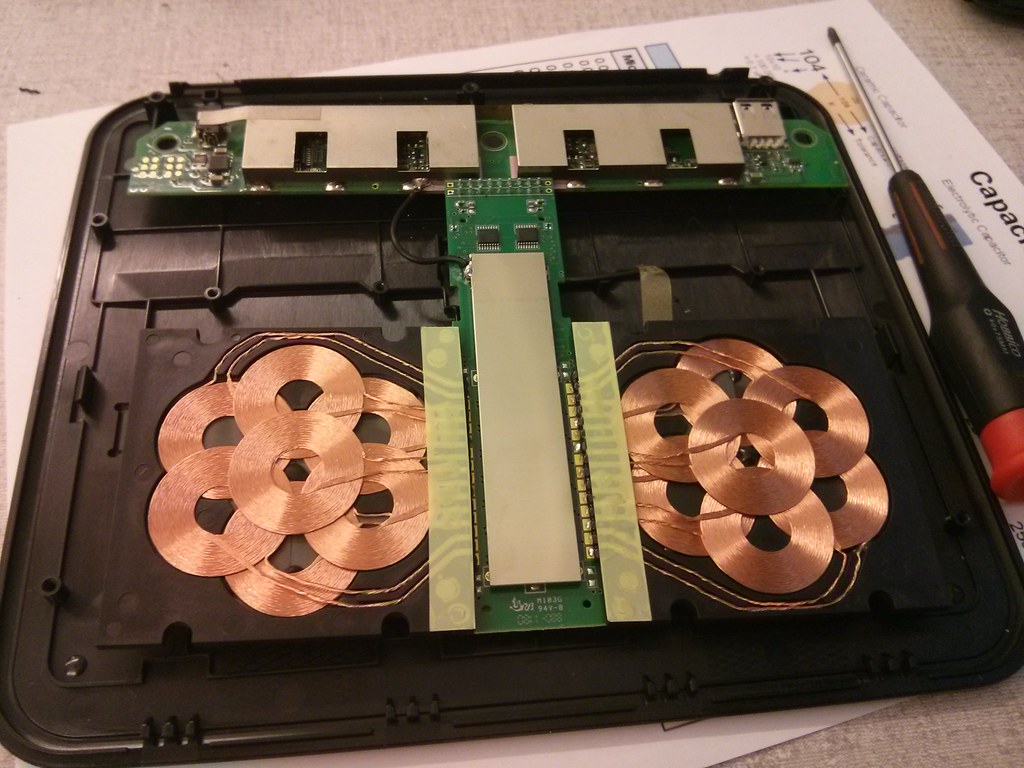
In addition to convenience and aesthetics, wireless charging also has durability advantages. Traditional charging cables are prone to wear and tear over time, often leading to frayed wires or damaged ports. Wireless charging mitigates these issues by reducing the physical connection between the charger and the device. By minimizing the need for constant plugging and unplugging, wireless charging can potentially extend the lifespan of both the device and its accessories.
Challenges and Limitations of Wireless Charging
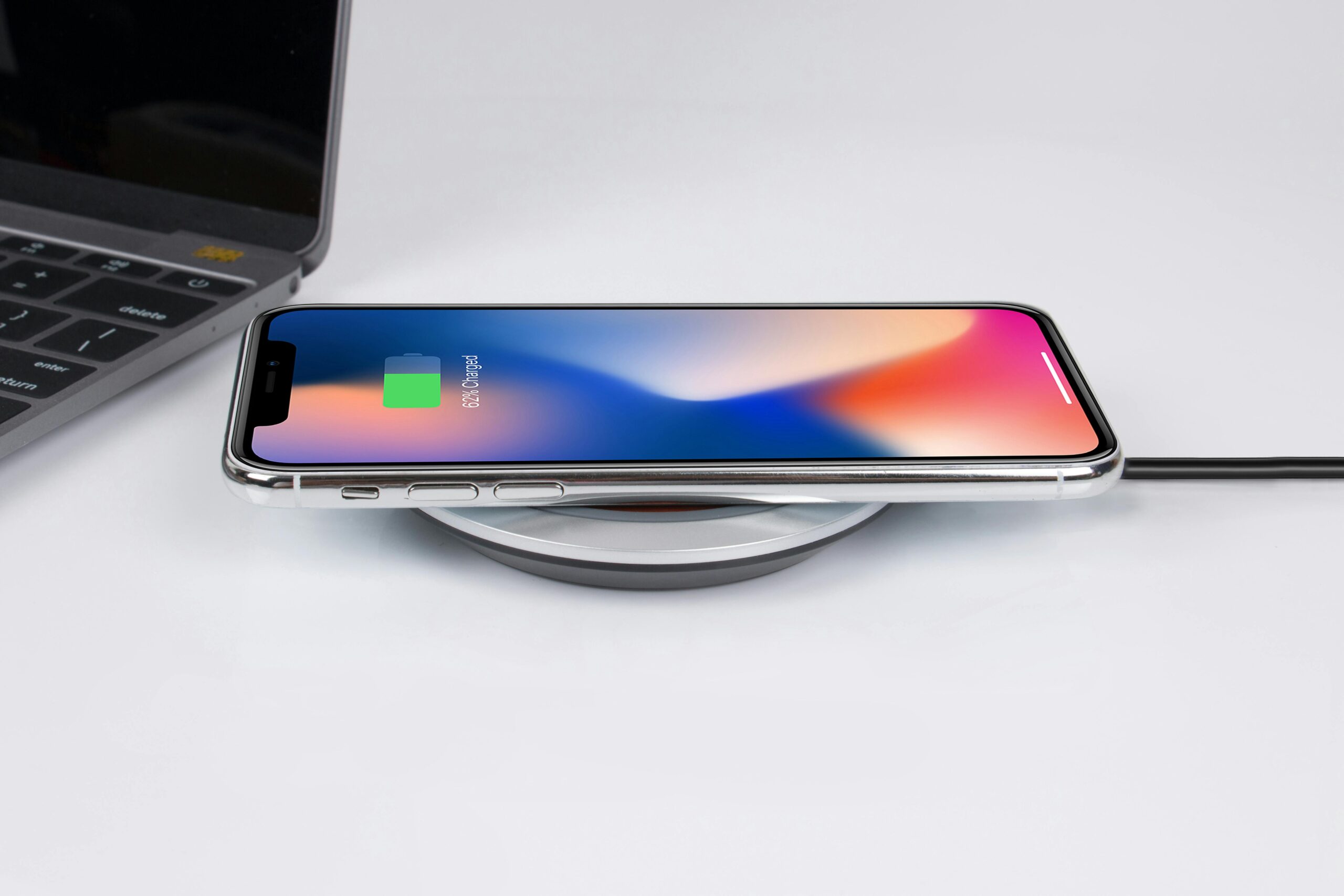
However, despite its numerous advantages, wireless charging is not without its challenges. One significant drawback is the slower charging speed compared to traditional wired methods. While advancements such as fast wireless charging are progressing, many users still rely on standard cables for a quick power boost. This reality can be particularly frustrating for individuals who are always on the go and need their devices charged in a hurry.

Another issue surrounds compatibility and standards. While the Qi standard has gained prominence and is widely adopted, the proliferation of different wireless charging technologies can lead to compatibility concerns. Not all devices support all wireless charging methods, which can frustrate users who may find themselves unable to charge their devices on certain pads. This lack of universal compatibility can hinder the widespread adoption of wireless charging solutions, especially in mixed-device environments.
The Need for Standardization
To address these challenges, there is a growing call for standardization across the wireless charging industry. By creating a unified standard that ensures compatibility across various devices, manufacturers can simplify the user experience and encourage broader adoption. Initiatives to promote universal designs could lead to the development of charging pads that accommodate a wide range of devices, ultimately reducing consumer frustration.
Environmental Considerations
As we evaluate the impact of wireless charging on our daily lives, it is also crucial to consider its environmental implications. The move toward wireless technology could reduce electronic waste by decreasing the demand for traditional chargers and cables. However, the production and disposal of wireless charging devices still contribute to electronic waste, making it essential for manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices.
Moreover, energy efficiency is a critical factor. Wireless charging systems can experience energy loss during the power transfer process, which may result in higher energy consumption compared to wired charging. Users and manufacturers alike must consider this aspect to ensure that the benefits of convenience do not come at the expense of sustainability. The development of more efficient wireless charging technologies could mitigate these concerns, making the technology more appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
The Future of Wireless Charging
Looking ahead, the future of wireless charging is promising yet complex. The technology is poised to play a pivotal role in various sectors, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics. As industries explore the integration of wireless charging capabilities into their products, we can expect innovations that prioritize user experience, efficiency, and sustainability.
For example, in the automotive realm, wireless charging pads embedded in parking spaces could offer seamless charging solutions for electric vehicles. Imagine driving into your garage and having your car charge automatically without the need to plug it in. Such advancements could revolutionize the way we think about energy consumption and convenience.

Furthermore, healthcare facilities are beginning to leverage wireless charging to enhance operational efficiency. With devices such as medical equipment requiring constant power, integrating wireless charging could streamline processes and improve patient care.
A Technology on the Rise
Wireless charging is a remarkable technology that offers convenience, flexibility, and innovative possibilities. While it comes with its set of challenges, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. As we continue to explore and implement this technology across various domains, we must also advocate for standardization, efficiency, and sustainability.

Embracing wireless charging means accepting a future where power is invisibly integrated into our surroundings, enhancing our daily experiences and reducing clutter. As advancements in wireless charging continue, we can look forward to a time when it will be not only a convenience but also a necessity in our daily lives. Whether at home, work, or on the go, wireless charging demonstrates that technology can evolve to meet our changing needs and preferences. The future is undoubtedly bright, with limitless possibilities.
Related posts:
1 Invisible Wireless Charger by Kew Labs
Checking Your Phone’s Compatibility with Wireless Charging
How Does Wireless Charging Work: A Comprehensive Guide